Android 7.0 Nougat will start to roll out to devices in August 2016. The changes are relatively minor (at least, compared to previous updates).
However, one of the biggest features affects the rooted Android community. Android 7.0 Nougat comes with a controversial new feature called verified boot.
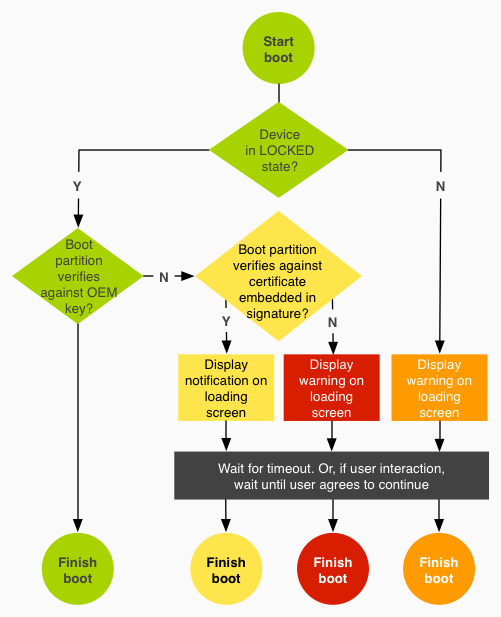
This feature is being bundled up as a security platform: basically, verified boot will check the “cryptographic integrity” of your phone to determine if someone has accessed the root directories.
Up to this point, Google has always had a laissez faire attitude towards rooting: they’ve allowed it and let rooted Android users continue using rooted devices free of restrictions. However, they’ve never made it easy. Developers like Samsung have taken a similar (although heavier-handed) approach).
So how does verified boot work? Let’s take a closer look.
How Does Verified Boot Work?
Verified boot checks the cryptographic integrity of your device to determine if it has been tampered with.
Now, that doesn’t specifically pertain to rooting. It checks multiple parts of your device for multiple security breaches. However, rooting certainly falls under the category of disrupting the cryptographic integrity.
Why does rooting affect the cryptographic integrity of your device? Well, rooting your phone involves modifying system files in order to introduce a new class of user with elevated permissions (i.e. “superuser” access).
Superuser access is disabled in ordinary versions of Android for security purposes.
In the hands of most moderate to advanced users, rooted devices are actually more secure. However, beginner users might experience a range of security problems – like infrequent updates that expose them to new malware.
Rooting also affects the boot image, which is where the kernel is stored. The kernel is the core component of the Android operating system. Most rooted Android users target the kernel simply to give themselves root access. But hackers might target the kernel to install their own compromised version of Android.
Google wants to prevent superuser access to make its devices safer. Rooted users want to maintain rooted access for all of the many rooting benefits.
Verified Boot Triggers an Error if a Single Byte is Corrupt
Verified boot is, understandably, sensitive to any changes in the cryptographic integrity of Android.
The system is so sensitive that if even one byte is detected as corrupt, verified boot will trigger an error message.
Vendors are expected to embrace verified boot, as they’re not exactly big fans of Android users rooting their phones. However, it’s unknown if some manufacturers will disable this feature – or at least make it an option for consumers.
Ultimately, rooted Android users in Android 7.0 Nougat are missing out simply because hacking a phone (say, for malicious purposes) and rooting involves the same basic process.
Google Wants Android to Appeal to Enterprise Users
Enterprise users are increasingly switching away from Apple (and even Blackberry) to Android. If Google wants people to take Android’s security seriously, then it needs to prevent people from hearing about security concerns caused by rooted Android.
Google also wants to prevent enterprise users from being shipped compromised phones – like knockoffs from China that come with malware installed out-of-the-box.
One Click Root Will Continue Working as Normal
Fortunately for us here at One Click Root, Android 7.0 Nougat doesn’t change the way we do things. You can still enjoy a world-class rooting experience customized to your unique device. Download our software today and discover how easy rooting Android 7.0 – or any version of Android – can be.
In any case, you can learn more about Verified Boot at the Android developers’ blog here.